The CAMDA Challenges
As traditional in CAMDA contests, neither we nor the producers of the data can provide advice on the datasets to individuals as dealing with the files forms part of the analysis challenge. There is, however, an open forum for the free discussion of the contest data sets and their analysis, in which you are encouraged to participate. For CAMDA 2016, we have have compiled the following exciting contests:
- The Oxford Nanopore ‘wiggle space’ challenge: Several samples had their DNA sequenced by Nanopore long read next-next-generation sequencing as well as more established sequencing technology. This is then to be evaluated on a 'mystery' sample of patient microbiota.
- The FDA SEQC neuroblastoma study: A comparison of RNA-seq and Agilent microarray gene expression profiles for clinical endpoint prediction (Zhang et al, Genome Biology 2015) assessed 498 children patients.
- The FDA SEQC consortium also provides a toxicogenomics study with matched NGS and microarray profiles for the response of over 100 rat livers to 27 chemicals with 9 different modes of action. This year the challenge focus is on exploiting alternative transcripts.
Please notice that CAMDA challenges are not limited to questions proposed here. We look forward to a lively contest!
Challenge 1: The Oxford Nanopore ‘wiggle space’ challenges
The Oxford Nanopore ‘wiggle space’ challenge (Mason lab, New York, original unpublished data). Several gut microbiota samples had their DNA sequenced by Nanopore long read next-next-generation sequencing as well as more established sequencing technology. Additional ‘mystery’ samples provide an independent blind test.
Questions of interest include, but are not limited to
- Technical: Improve base-calling, assembly, and signal level models of the Nanopore data with the reference sequences and/or Illumina sequencing serving as benchmark. We have samples with biological and samples with technical replicates.
- Biological: Meta-genomics: Detection, discrimination, and abundance quantification of species. For some training samples, relative abundances are known (synthetic mixes). Sequence / functional predictive analysis of pathogenicity. And: Analysis and identification of the ‘mystery’ sample!
Data download For this challenge, raw data are provided together with sample description file. Participants who want to use this dataset should read and accept the data download agreement to get access.
Challenge 2: Sequencing Quality Control neuroblastoma studys
Sequencing Quality Control neuroblastoma study (SEQC, Fischer lab, Köln). A comparison of RNA-seq and Agilent microarray gene expression profiles for clinical endpoint prediction (Zhang et al, Genome Biology 2015) assessed 498 children patients. The published summary data are complemented by raw signal level data sets for sequencing and arrays, and extended clinical meta-data (event-free & overall survival times, multiple prognostic markers, therapy data). In addition, we newly provide: whole genome shotgun (WGS) data of 56 patients for both cancer tissue and normal cells (~30x coverage), and array CGH data of 200 patients (for CNV and SNP analysis). Challenge ideas:
- Technical: Compare quantitative expression profiling at different levels: probe / NGS read, gene, transcript, functional/pathway, prognostic performance.
- Biological: Better survival time prediction by effective data integration or improved transcript level models. Advance our understanding of the mechanisms behind cancer progression or therapy response by effective data integration, a first comprehensive transcript level analysis, or novel functional (network/pathway) analysis.
Challenge 3: SEQC Rat TGx - rat liver response to chemicals
The FDA SEQC consortium has compiled a series of synthetic benchmarks and applied use-cases to assess the performance of modern gene transcript expression profiling methods, for the first time systematically assessing RNA-Seq in a wider context.
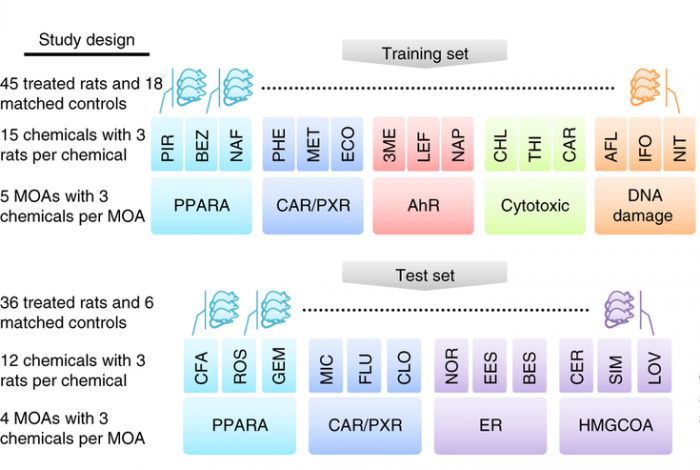
In this study, matched RNA-Seq and microarray gene expression profiles were collected of 105 rat livers to test their response to 27 chemicals representing 9 different modes of action (MOA). The NGS reads collected comprise 1.5 Terabases. In the study, a key question was the predictability of the chemical mode of action. Initial platform comparison showed consensus as well as variation, and effects of data processing were not yet further explored.
Data Description
This data comprised a training set and a test set with the text on the left detailing the experimental design and the text on the right listing the key analyses conducted (see figure below). Both microarray and RNA-seq were used to profile transcriptional responses induced by treatment of rats by each chemical; each is associated with a specific mode of action (MOA). For each MOA there were three representative chemicals and three biological replicates per chemical. Cross-platform concordance was evaluated at multiple levels: deferentially expressed genes, mechanistic pathways and MOAs. To compare the predictive potential of RNA-seq and microarray as gene-expression biomarkers, four MOAs by both platforms were analyzed as a test set. Two of the MOAs (PPARA and CAR/PXR) were present in the training set whereas the other two were not.
Reference:
- C. Wang et al. (2014). A comprehensive study design reveals treatment- and abundance-dependent concordance between RNA-Seq and microarray data., Nat. Biotechnol. 32, 926-932. (link to article)
Questions of interest include, but are not limited to
- Topic 1: Inter-platform concordance: Is a shared list of genes the ‘golden standard’ to test the cross-platform consistency of the underlying biology? What biological insights are unique to data from one of the two platforms? Can we understand or adjust for that?
- Topic 2: Classification / prediction: We know we can get 100% accurate prediction of the chemical mode of action for RNA-Seq. Can you develop a similarly good predictor that works cross-platform?
- Topic 3: Alternative splicing: What can we learn about the role of alternative splicing from the RNA-Seq data?
Data download For this challenge, raw and processed data are provided as separate packages. The data packages contain metadata files, and either processed or raw data folders. Participants who want to use this dataset should read and accept the data download agreement to get access.